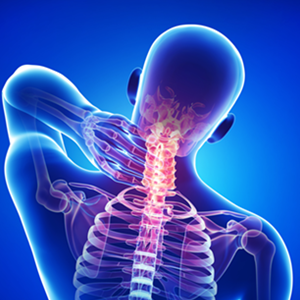
Osteopathy is a natural method that appeared in the United States in the late nineteenth century from the hand of Dr. Andrew Taylor Still. According to him, the mechanical principles on which osteopathy is based are as old as the human being. These principles are:
• The unity and wholeness of the body.
• The interrelationship of structure and function.
• The self-healing capacity of the body.
• The rule of the artery is supreme.
Osteopathy emphasizes on the wholeness of the body, believes and proves the close relationship existing among all the systems in the organism. A disruption on any part of the organism can affect a different one or even all of the systems. Osteopathy defends a global treatment of the body is the only way to achieve its correct functioning.
Throughout his life and studies, Andrew Taylor Still explained the important relationship between the body‘s structure and functions. He believed that any dysfunction in the structure, caused by whichever factor, would lead to the wrong functioning of the organism and that this imbalance would be the cause for the disease to appear.
“The osteopath reasons, if he reasons at all, that order and health are inseparable, and that when order in all parts is found, disease cannot prevail” -- A. Taylor Still
The main goal of an osteopath is to be an expert on the human body and to perfectly understand his or her task: to restore the balance of the structure in need. This will help the body itself to balance its functions and cure the disease. In order to achieve this, the osteopath has to ensure that the damaged parts of the body recover their proper blood circulation and waste removal through the circulatory and lymphatic systems, leading to the solving of the problem and the patient’s improvement.
Osteopaths are experts in charge of the human body’s health who, thanks to their osteopathic manual therapies, help people recover proper health conditions.